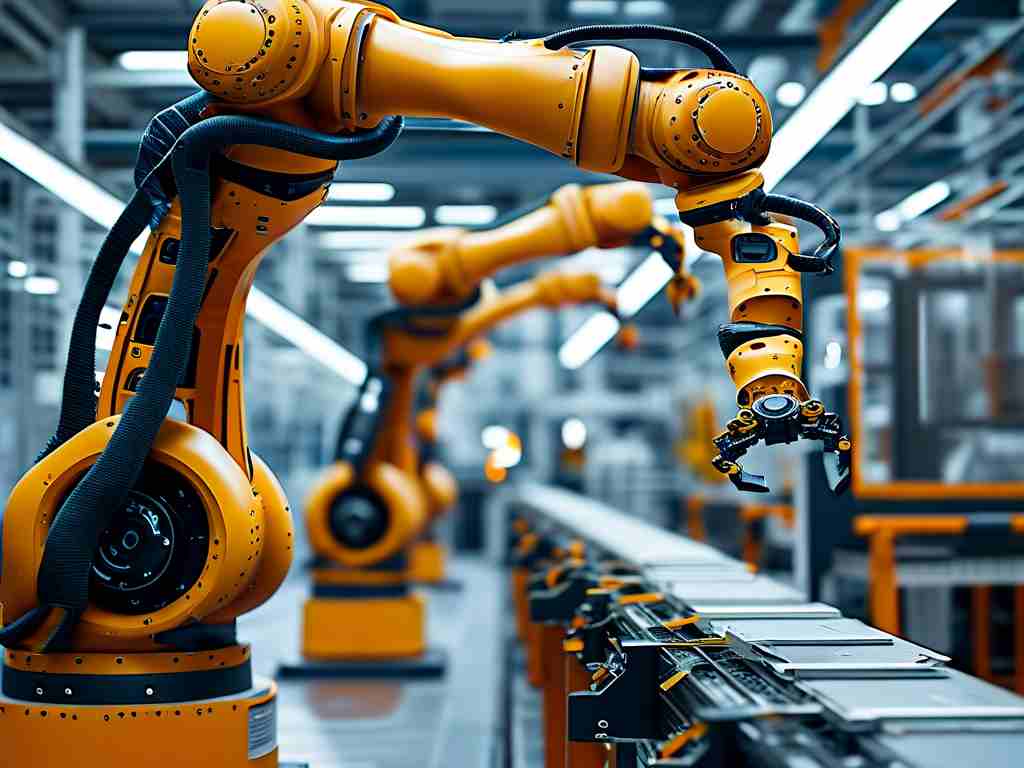
The automotive industry stands at the forefront of technological evolution, with robotics emerging as a transformative force. From assembly lines to quality control, car manufacturers are leveraging advanced robotic systems to redefine efficiency, precision, and scalability. This shift not only addresses production challenges but also reshapes the competitive landscape of global automotive markets.
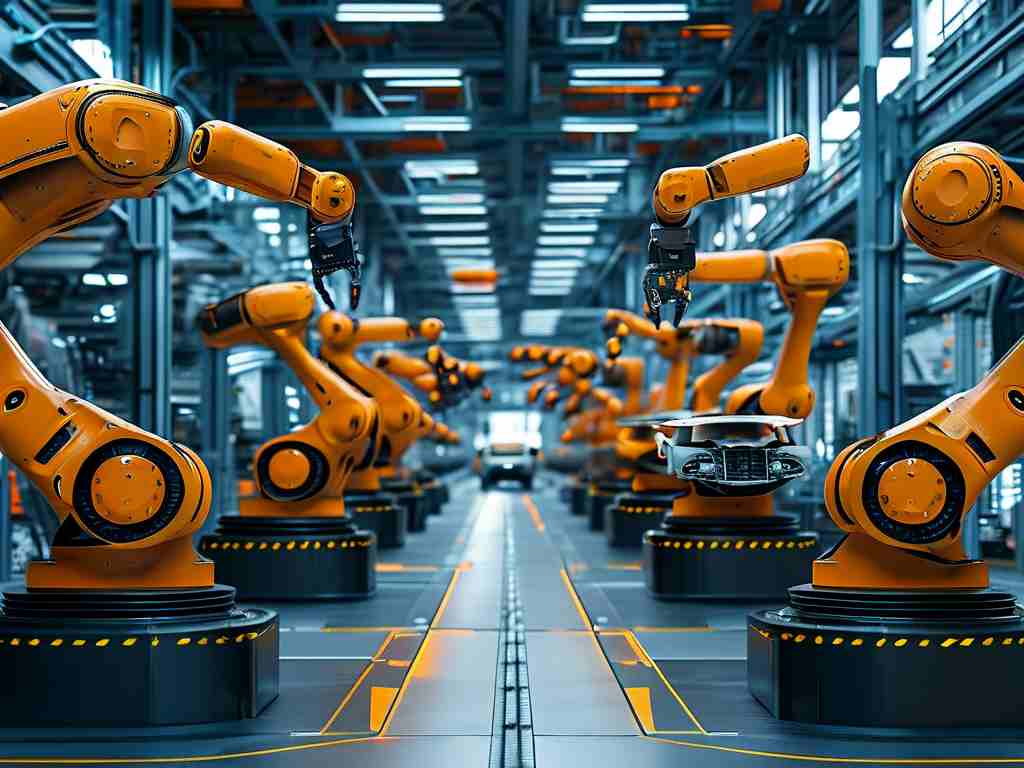
Precision Engineering in Production
Modern automotive factories now deploy robotic arms equipped with AI-driven vision systems capable of detecting submillimeter defects in vehicle components. For instance, Tesla’s Gigafactories utilize custom-designed robots that perform 90% of welding tasks with near-zero error margins. Unlike traditional machinery, these systems adapt in real time to variations in material thickness or environmental conditions, reducing waste by up to 40%. Collaborative robots (cobots), such as those used by BMW, work alongside human operators to install intricate electrical systems, merging human dexterity with machine consistency.
Supply Chain Optimization
Beyond the factory floor, robotics plays a pivotal role in logistics. Autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) at Toyota’s facilities transport parts between warehouses and assembly stations with minimal human intervention. These AGVs use LiDAR and machine learning algorithms to navigate dynamic environments, cutting downtime caused by misplaced inventory. Similarly, Ford’s “Smart Warehouse” initiative employs drones for inventory audits, completing tasks 8x faster than manual methods. Such innovations are critical as automakers face pressure to deliver vehicles amid fluctuating supply chain demands.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its benefits, robotic integration presents hurdles. High initial costs remain a barrier for smaller manufacturers—a single industrial robot can exceed $250,000. Additionally, workforce displacement remains contentious. While companies like Volvo reskill employees to oversee robotic systems, labor unions argue that automation could eliminate 15% of traditional assembly jobs by 2030. Cybersecurity is another concern; interconnected robotic networks are vulnerable to hacking, as seen in a 2022 breach at a European OEM that halted production for 72 hours.
The Future: Human-Robot Synergy
Forward-thinking automakers are exploring symbiotic workflows. Hyundai’s “Metaplant” concept combines exoskeleton-assisted workers with robots handling hazardous tasks like battery acid handling. Meanwhile, startups like Boston Dynamics are testing mobile robots for post-production inspections, capable of climbing into vehicle chassis for quality checks. As 5G connectivity expands, remote-controlled robotics could enable experts to troubleshoot assembly issues from continents away, further blurring geographical constraints.
Environmental Impact
Robotic technologies also contribute to sustainability goals. Mercedes-Benz uses solar-powered robots for painting, reducing CO₂ emissions by 30% per vehicle. Recycling robots, such as those developed by ABB, disassemble end-of-life cars to recover metals and batteries, supporting circular economy initiatives. These advancements align with global regulations pushing for greener manufacturing practices.
In , robotic technologies are not merely tools but strategic assets reshaping automotive manufacturing. While challenges persist, the fusion of AI, mobility, and human expertise promises a future where cars are built smarter, cleaner, and faster than ever before. As competition intensifies, automakers who master this balance will lead the race toward tomorrow’s mobility solutions.