The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with industrial robotics is transforming production lines across global manufacturing sectors. Unlike traditional automated systems limited to repetitive tasks, AI-enhanced robots now demonstrate unprecedented adaptability, precision, and decision-making capabilities. This technological synergy addresses long-standing challenges in quality control, operational efficiency, and workforce safety while opening new frontiers for smart factories.
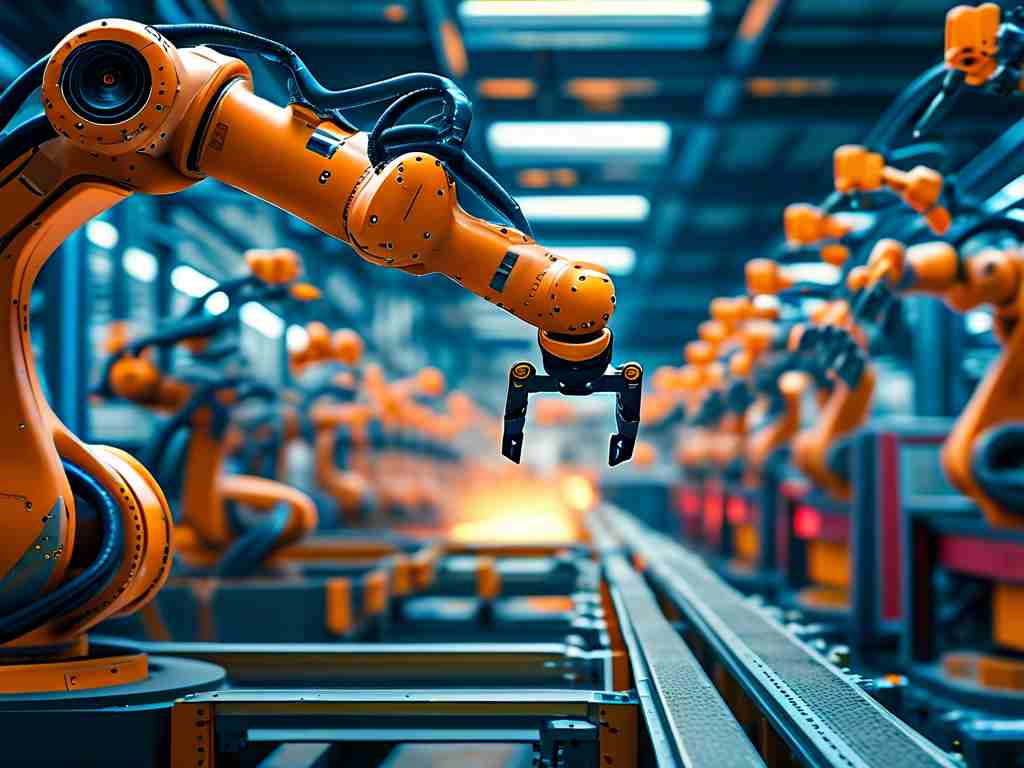

At the core of this evolution lies machine learning algorithms that enable robots to interpret sensor data in real time. For instance, automotive assembly lines now deploy vision-based AI robots capable of detecting micron-level defects in vehicle chassis components – a task previously requiring human inspectors. These systems analyze thousands of product images per hour, continuously improving defect recognition accuracy through neural network training.
Another breakthrough emerges in predictive maintenance applications. AI-powered collaborative robots (cobots) monitor vibration patterns, thermal signatures, and energy consumption metrics from industrial equipment. By cross-referencing this data with historical performance records, these systems can forecast mechanical failures up to 72 hours in advance. A case study from a German semiconductor plant revealed a 40% reduction in unplanned downtime after implementing such AI-driven maintenance protocols.
The flexibility of AI-industrial robotics shines in customized production scenarios. Traditional robotic arms required extensive reprogramming for product variations, but AI-enabled units can now adapt workflows autonomously. A notable example comes from a Japanese electronics manufacturer where robots reconfigure assembly paths within minutes when switching between 15 different smartphone models, achieving 98.6% first-pass yield rates.
Safety enhancements represent another critical advancement. Deep reinforcement learning allows robots to dynamically adjust movement trajectories based on human worker proximity. In a recent implementation at a U.S. aerospace facility, AI-controlled robotic welders reduced near-miss incidents by 83% while maintaining production speeds. The system’s spatial awareness algorithms process lidar and depth camera inputs at 60 frames per second to ensure collision-free operation.
Despite these advancements, challenges persist in AI-robotics integration. Data security concerns escalate as networked robots handle sensitive production information. Leading manufacturers are adopting blockchain-based verification systems to protect intellectual property embedded in robotic programming. Additionally, workforce adaptation remains crucial – a 2023 industry survey indicates 67% of manufacturers now run upskilling programs focused on AI-robotics supervision.
Looking ahead, the convergence of 5G connectivity and edge computing promises to amplify AI-robotics capabilities. Low-latency networks enable real-time coordination between robot swarms, while on-device processing enhances data privacy. Experimental projects in China’s manufacturing hubs already demonstrate multi-robot systems completing complex assembly tasks 30% faster through distributed AI decision-making.
Ethical considerations are gaining prominence as AI-robotics systems assume more decision-making roles. The European Commission recently proposed guidelines for “explainable AI” in industrial settings, requiring robots to log decision rationale during abnormal production scenarios. This transparency initiative aims to maintain human oversight while leveraging AI’s analytical strengths.
The environmental impact of AI-driven robotics also warrants attention. Next-generation robots optimize energy consumption patterns using genetic algorithms, with pilot projects showing 22% reduction in factory power usage. Simultaneously, AI systems are being deployed to improve recycling processes – robotic waste sorters powered by computer vision now achieve 95% material classification accuracy in Scandinavian recycling plants.
As industries approach Industry 4.0 maturity, the fusion of AI and robotics continues to redefine manufacturing paradigms. From self-optimizing production cells to AI-generated robotic control code, these technologies are not merely automating tasks but fundamentally reimagining how goods are designed, produced, and delivered. Enterprises adopting these solutions report average productivity gains of 35-40%, positioning AI-industrial robotics as a cornerstone of competitive manufacturing strategy.
Future developments may see quantum computing-enhanced AI robots solving currently intractable optimization problems, while advances in neuromorphic engineering could yield robots with human-like tactile sensitivity. As these technologies mature, the boundary between human and machine capabilities in industrial settings will continue to evolve, creating both opportunities and challenges for global manufacturing ecosystems.