Upgrading a computer's memory (RAM) is one of the most effective ways to breathe new life into aging systems or optimize newer machines for demanding tasks. This article explores the practical steps and considerations for successfully installing additional RAM modules while highlighting the performance improvements users can expect.
Understanding RAM and Its Impact
Random Access Memory (RAM) serves as a computer's short-term data storage, temporarily holding information that active applications and processes require. When a system runs low on available RAM, it compensates by using slower storage devices like hard drives or SSDs as virtual memory, leading to noticeable lag. By expanding physical memory capacity, users enable smoother multitasking, faster application launches, and improved responsiveness in memory-intensive workflows such as video editing, 3D rendering, or modern gaming.
Preparation Steps
Before purchasing new RAM modules, verify compatibility with your motherboard. Check manufacturer specifications for supported memory types (DDR4/DDR5), maximum capacity, and speed limits. Tools like CPU-Z provide detailed system information:
1. Download and run CPU-Z
2. Navigate to the "Memory" and "SPD" tabs
3. Note current RAM configuration and available slots For laptop users, consult device documentation regarding upgradability – some ultra-thin models have soldered memory that cannot be modified.
Installation Process
- Power Down Safely: Shut down the computer and disconnect all cables. Press the power button for 10 seconds to discharge residual electricity.
- Access Memory Slots: Desktop users typically remove the side panel, while laptop configurations vary – some require bottom cover removal or keyboard detachment.
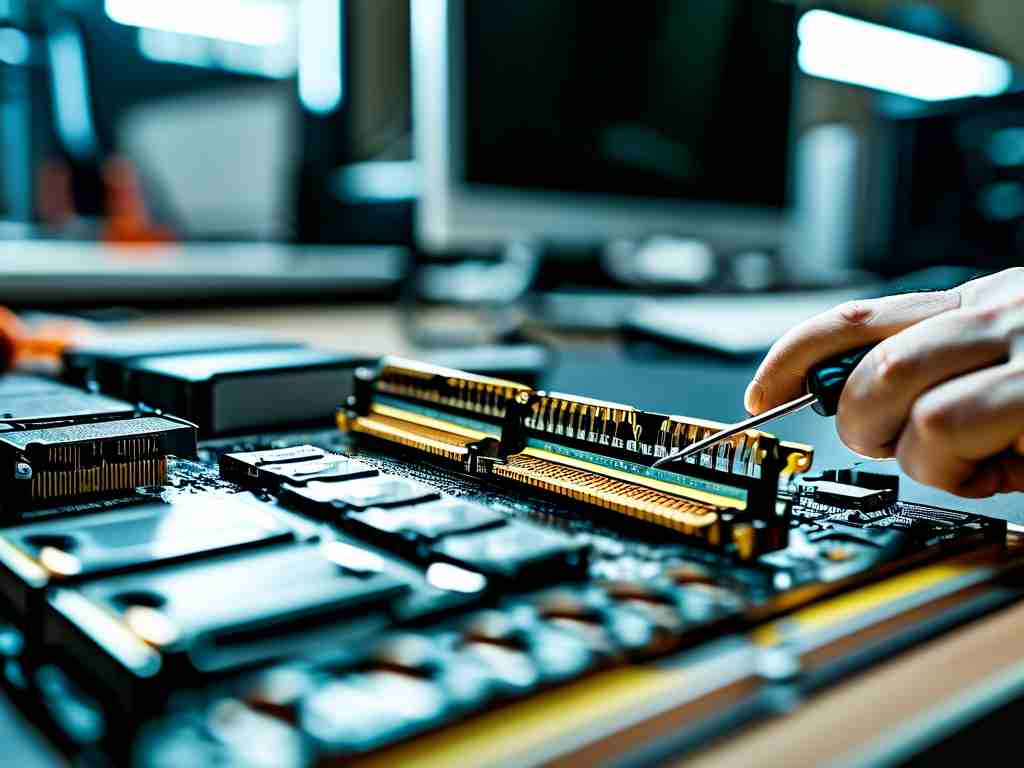
- Handle Modules Carefully: Hold RAM by the edges to avoid static damage. Align the notch on the module with the slot key and apply firm, even pressure until retention clips engage.
- Post-Installation Check: Reassemble the device and power it on. Verify recognition in the operating system:
- Windows: Task Manager > Performance > Memory
- Linux: Terminal command
sudo dmidecode --type memory
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If the system fails to boot or doesn't recognize new memory:
- Reseat modules to ensure proper connection
- Test individual sticks in different slots
- Reset BIOS/UEFI settings to default
- Update motherboard firmware if addressing compatibility issues
Performance Expectations
Real-world improvements depend on usage patterns:
- General computing: 8GB → 16GB reduces file swap delays
- Content creation: 32GB+ allows seamless 4K video editing
- Gaming: Matches GPU intensity – 16GB is current sweet spot
For optimal results, pair RAM upgrades with SSD installations and regular system maintenance. Advanced users can enable XMP profiles in BIOS for certified speed boosts, though this may affect system stability if improperly configured.
Long-Term Considerations
Modern operating systems intelligently manage memory allocation, but users should periodically:
- Monitor usage patterns via built-in resource monitors
- Clean unnecessary background processes
- Consider future-proofing – DDR5 adoption grows as prices decline
While not a cure-all solution, RAM upgrades remain among the most cost-effective performance enhancements. Combined with strategic hardware updates and software optimization, memory expansion can extend a computer's usable lifespan by 2-3 years in many cases, making it a worthwhile investment for both casual and power users.