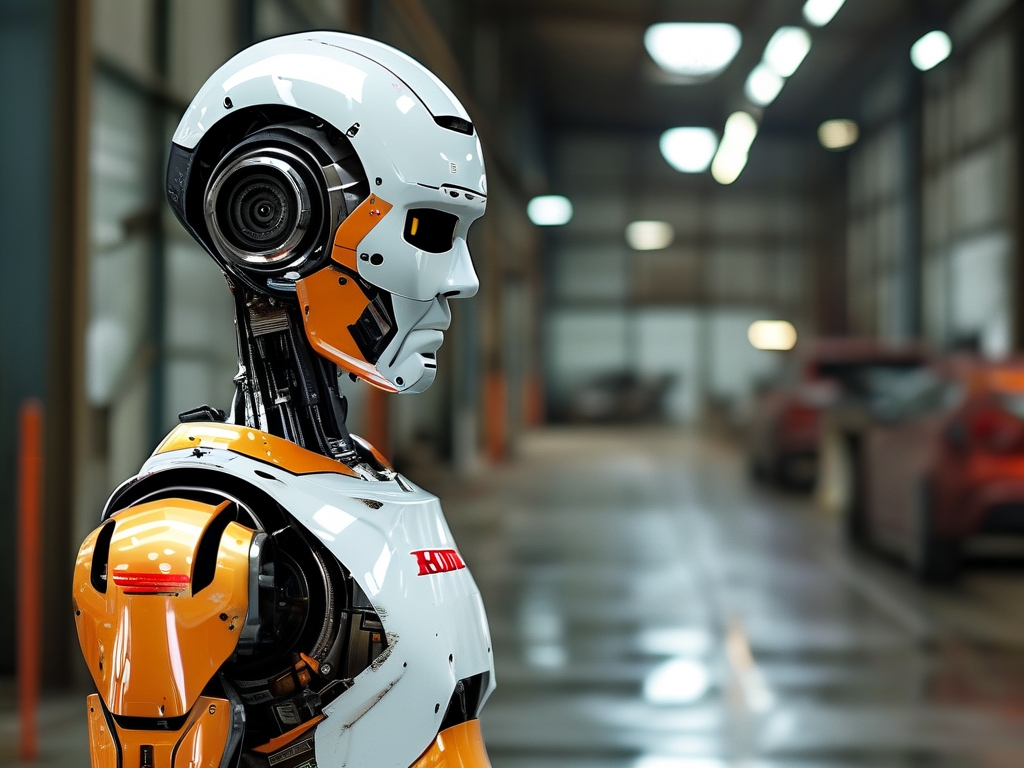
For decades, Honda has been synonymous with automotive innovation, but its contributions to robotics technology remain equally groundbreaking. From the iconic humanoid robot ASIMO to cutting-edge industrial automation systems, Honda’s robotics journey reflects a blend of engineering precision, biomimicry, and futuristic vision. This article explores the evolution, technical breakthroughs, and societal impacts of Honda’s robotics technology.
The Birth of ASIMO: A Humanoid Pioneer
Honda’s robotics ambitions began in 1986 with the E-series, a line of experimental bipedal robots. These early models focused on mastering basic walking mechanics, laying the foundation for the Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility (ASIMO), unveiled in 2000. Standing 130 cm tall and weighing 54 kg, ASIMO represented a quantum leap in robotics. Unlike rigid industrial robots, ASIMO was designed to interact with humans in dynamic environments. Its key innovations included:
- Dynamic Balance Control: Using proprietary "i-WALK" technology, ASIMO achieved fluid walking, running, and stair-climbing by continuously adjusting joint angles and center of gravity.
- Predictive Movement Algorithms: Sensors in its feet and torso enabled real-time terrain adaptation, preventing falls on uneven surfaces.
- Human-Centric Interaction: ASIMO could recognize faces, interpret gestures, and respond to voice commands—a precursor to modern AI assistants.
By 2011, ASIMO’s capabilities expanded to include sprinting at 9 km/h, hopping on one leg, and even serving coffee—a symbolic fusion of practicality and showmanship.
Beyond ASIMO: Expanding Robotics Applications
While ASIMO captured global attention, Honda quietly diversified its robotics portfolio. The E2-DR, a disaster-response robot unveiled in 2017, exemplifies this shift. Designed for hazardous environments, the E2-DR can traverse rubble, climb ladders, and operate for 90 minutes in heavy rain. Its modular design allows customization for firefighting, nuclear inspections, or search-and-rescue missions.
Another milestone is Honda’s Walking Assist Device, a lightweight exoskeleton targeting mobility-impaired users. Using ASIMO-derived balance algorithms, it redistutes weight to reduce joint strain, offering a glimpse into healthcare robotics.
Technical Innovations Driving Honda’s Success
1. Biomimetic Engineering
Honda’s robots often emulate human anatomy. ASIMO’s articulated fingers, for instance, replicate tendon-driven dexterity, enabling object manipulation. Similarly, its “toe-joint” mechanism mimics the human foot’s push-off motion for efficient gait cycles.
2. Sensor Fusion and AI Integration
Honda integrates lidar, cameras, and inertial measurement units (IMUs) to create spatial awareness. In the Honda Autonomous Work Vehicle, these systems enable navigation in GPS-denied environments like construction sites. Machine learning further optimizes decision-making—a feature highlighted in Honda’s 2023 partnership with Sony to develop AI-driven service robots.
3. Energy Efficiency
Robotics demands power-density breakthroughs. ASIMO’s 2014 upgrade featured a 40% lighter lithium-ion battery and brushless motors, extending operation time to 60 minutes. Honda’s fuel cell research, initially for cars, now informs hydrogen-powered drones and logistics robots.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite progress, Honda faces hurdles. Bipedal robots remain energy-intensive compared to wheeled counterparts, limiting industrial adoption. Public perception is another barrier; while ASIMO charmed audiences, its $2.5 million development cost sparked debates about commercial viability.
Ethically, Honda emphasizes “collaborative robotics”—systems that augment human labor rather than replace it. This philosophy underpins projects like the Honda UNI-CUB, a self-balancing personal mobility device designed for coexistence in pedestrian spaces.
The Future: Humanoid Robots and Society
Honda recently shifted focus from entertainment-oriented robots to functional applications. In 2024, it announced a factory-trained humanoid robot capable of assembling car components—a direct synergy with its automotive expertise. This robot leverages ASIMO’s agility but prioritizes cost-effectiveness and safety certifications for industrial use.
Meanwhile, Honda invests in cognitive robotics, aiming to create machines that understand context and intent. A 2022 prototype demonstrated a robot that fetches tools based on a mechanic’s gaze direction—a step toward intuitive human-robot teamwork.
Honda’s robotics journey—from ASIMO’s dance routines to life-saving E2-DR robots—reveals a relentless pursuit of innovation. By blending mechanical ingenuity with human-centered design, Honda not only advanced robotics but also redefined how humans and machines interact. As AI and material science evolve, Honda’s next chapter may well bridge the gap between laboratory marvels and everyday utility, transforming industries from healthcare to urban mobility.
Word count: 1,023


