The integration of robotics into the food service industry has revolutionized how meals are delivered to customers. From automated conveyor belts in sushi restaurants to autonomous mobile robots in high-end hotels, robotic food service technology combines precision engineering, artificial intelligence, and user-centric design. This article explores the technical foundations, operational challenges, and real-world applications of these systems.
Navigation and Spatial Awareness
At the core of robotic food service is advanced navigation technology. Most systems rely on simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithms, which enable robots to create real-time maps of dynamic environments like crowded dining areas. For instance, the AIC-AI robot series uses lidar sensors paired with infrared cameras to detect obstacles as small as 10 cm in height, ensuring smooth navigation around chairs and foot traffic. Unlike traditional automated guided vehicles (AGVs) that follow magnetic tapes, modern food service robots employ adaptive pathfinding, recalculating routes within 200 milliseconds when encountering unexpected barriers.
Payload and Stability Mechanisms
Delivering dishes without spills requires sophisticated stabilization systems. The Servi robot by Bear Robotics incorporates a three-axis gyroscopic tray that adjusts to movement angles up to 15 degrees, capable of carrying 15 kg across uneven flooring. This is achieved through a combination of servo motors and pressure-sensitive grip pads that secure plates during abrupt stops. Experimental models are testing magnetic levitation trays that reduce friction-induced vibrations, though these remain cost-prohibitive for most commercial deployments.
Human-Robot Interaction Design
Successful implementation hinges on intuitive user interfaces. Many systems now feature multilingual touchscreens and voice command compatibility. A case study from Singapore’s Haidilao hot pot chain revealed that 72% of customers preferred robot servers with anthropomorphic features like eye-level displays and modulated voice tones. However, designers must balance engagement with functionality—overly complex animations or verbose interactions can slow service speeds.
Energy and Maintenance Considerations
While robotic systems reduce labor costs, they introduce new operational demands. The average food service robot consumes 1.2 kWh during an 8-hour shift, requiring strategically placed charging stations. Cloud-connected diagnostic systems have become critical; for example, Pudu Robotics’ platform analyzes motor performance data to predict maintenance needs with 89% accuracy, minimizing downtime. Some restaurants now employ hybrid fleets, using smaller robots for beverage delivery and larger units for main courses to optimize energy use.
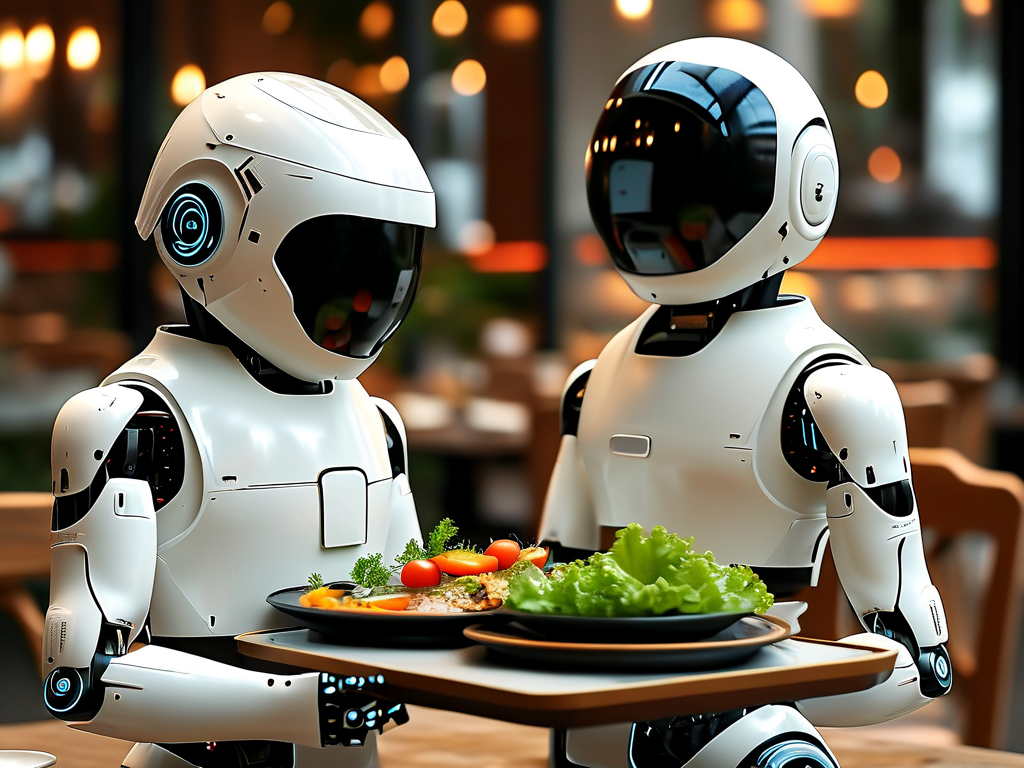

Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Meeting food safety standards presents unique challenges. In the European Union, robotic food handlers must comply with EN 1672-2 sanitation requirements, necessitating waterproof casings and antimicrobial surface coatings. California’s SB 1467 mandates emergency stop buttons within 1.2 meters of any operating robot in public spaces. Recent advancements include UV-C sterilization modules that activate during return trips to kitchen stations.
The future of robotic food service lies in swarm intelligence systems. Researchers at MIT’s CSAIL lab demonstrated a coordinator algorithm allowing 12 robots to collaboratively serve a 200-seat banquet hall with 40% fewer collisions than individual units. As 5G connectivity and edge computing mature, expect tighter integration between kitchen management software and robotic fleets, potentially reshaping entire service workflows.
While skeptics argue about the loss of human touch, industry data tells a different story. A 2023 NRA report showed establishments using robotic servers achieved 22% higher table turnover rates during peak hours. As the technology evolves, the focus will shift from merely automating tasks to enhancing overall dining experiences through predictive service and personalized interactions.









